The Fascinating World of Astronomical Units
When exploring the vastness of space and the celestial bodies within it, astronomers and scientists often rely on a unit of measurement known as the astronomical unit (AU). This unit provides a convenient way to express distances within our solar system and beyond.
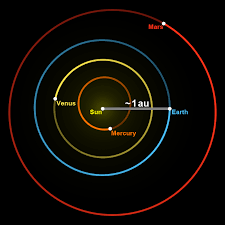
Defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, one astronomical unit is approximately 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers. This distance serves as a fundamental reference point for measuring distances to other planets, asteroids, comets, and other objects in space.
For example, the average distance from Mars to the Sun is about 1.52 astronomical units, while Jupiter is around 5.2 astronomical units away. By using AU as a standard unit of measurement, astronomers can easily compare and understand the vast scales of our solar system.
Outside of our solar system, astronomers use light-years to measure distances to stars and galaxies. However, within our cosmic neighbourhood, astronomical units provide a more practical and relatable scale for measuring distances.
As technology advances and space exploration continues to expand, the use of astronomical units remains crucial in understanding the complexities of our universe. From calculating planetary orbits to planning interplanetary missions, AU serves as an invaluable tool in unlocking the mysteries of space.
So next time you gaze up at the night sky and marvel at the wonders of our solar system, remember that astronomers around the world are using astronomical units to navigate and explore the depths of space.
Understanding Astronomical Units: Key FAQs Answered
- What is an astronomical unit (AU)?
- How is the astronomical unit defined?
- Why do astronomers use astronomical units?
- What is the average distance of one astronomical unit?
- How do astronomers measure distances using astronomical units?
- Are astronomical units used only within our solar system?
- Can you convert astronomical units to kilometers or miles?
- Why are astronomical units important in space exploration?
What is an astronomical unit (AU)?
An astronomical unit (AU) is a fundamental unit of measurement used in astronomy to represent the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. Defined as approximately 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers, the AU serves as a crucial reference point for measuring distances within our solar system. By providing a standard unit of measurement, astronomers can easily compare and understand the vast scales of planetary orbits, asteroid belts, and other celestial bodies in relation to the Sun. The concept of AU plays a vital role in space exploration and research, enabling scientists to navigate and explore the complexities of our cosmic neighbourhood with precision and accuracy.
How is the astronomical unit defined?
The astronomical unit is defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. This standard unit of measurement, approximately 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers, serves as a crucial reference point for astronomers when calculating distances within our solar system and beyond. By using the Earth-Sun distance as a fundamental benchmark, scientists can accurately measure and compare distances to planets, asteroids, and other celestial bodies in space. This definition of the astronomical unit plays a vital role in our understanding of the vast scales of the universe and aids in various astronomical calculations and observations.
Why do astronomers use astronomical units?
Astronomers use astronomical units as a standard unit of measurement to express distances within our solar system and beyond. By defining one astronomical unit as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is approximately 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers, astronomers have a convenient reference point for measuring distances to other planets, asteroids, comets, and celestial objects. This standard unit allows astronomers to compare and understand the vast scales of our solar system easily. Additionally, astronomical units play a crucial role in calculating planetary orbits, planning interplanetary missions, and navigating the complexities of space exploration.
What is the average distance of one astronomical unit?
One frequently asked question regarding astronomical units is, “What is the average distance of one astronomical unit?” An astronomical unit (AU) is defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, approximately 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers. This standard unit of measurement serves as a fundamental reference point for calculating distances within our solar system and plays a crucial role in understanding the vast scales of space. By knowing the average distance of one astronomical unit, astronomers can better comprehend the distances between planets, asteroids, and other celestial objects in relation to our Sun.
How do astronomers measure distances using astronomical units?
Astronomers utilise astronomical units (AU) as a fundamental measurement to determine distances within our solar system. By defining one AU as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers, astronomers can calculate the distances of other celestial bodies relative to this standard. For instance, they measure the distance from a planet to the Sun in AU by dividing the actual distance by the average Earth-Sun distance. This method allows astronomers to easily compare and comprehend distances within our cosmic neighbourhood, aiding in planetary exploration and research endeavours.
Are astronomical units used only within our solar system?
Astronomical units are primarily used within our solar system as a convenient measure of distance, with one AU representing the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. While AU is commonly employed to describe distances between planets, asteroids, and other objects within our solar system, it is not limited to these boundaries. Astronomers also use astronomical units to express distances to nearby stars and exoplanets, particularly when discussing planetary systems outside our own. Despite being rooted in solar system measurements, astronomical units serve as a versatile tool for understanding distances on both interplanetary and interstellar scales.
Can you convert astronomical units to kilometers or miles?
One frequently asked question regarding astronomical units is whether they can be converted to kilometres or miles. The answer is yes, astronomical units can be converted to kilometres or miles for a better understanding of the vast distances involved in space exploration. One astronomical unit is approximately equal to 150 million kilometres or 93 million miles, representing the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. By converting astronomical units to more familiar units of measurement like kilometres or miles, we can grasp the immense scales of our solar system and beyond, making it easier to comprehend the distances between celestial bodies in space.
Why are astronomical units important in space exploration?
Astronomical units play a vital role in space exploration due to their significance in measuring distances within our solar system. By providing a standard unit based on the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, astronomical units offer a practical way for scientists and engineers to calculate and compare distances to planets, asteroids, and other celestial bodies. This standardisation simplifies mission planning, spacecraft navigation, and orbital calculations, making it easier for space agencies to conduct successful interplanetary missions. Without the use of astronomical units, accurately navigating through the vastness of space would be significantly more challenging, highlighting the importance of this unit in advancing our understanding of the cosmos through space exploration.
No Responses