The Significance of Clusters in Data Mining
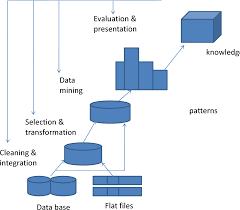
Data mining is a crucial process in extracting valuable patterns and information from large datasets. One of the key techniques used in data mining is clustering. Clustering involves grouping similar data points together based on certain characteristics or features.
Clusters play a vital role in data mining as they help identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By clustering data points that share common attributes, analysts can gain insights into the underlying structure of the dataset.
There are various types of clustering algorithms used in data mining, such as K-means, hierarchical clustering, and DBSCAN. Each algorithm has its strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for different types of datasets and applications.
Clusters can be visualised using scatter plots or other graphical representations to help analysts understand the relationships between data points. This visualisation is essential for interpreting the results of clustering algorithms and making informed decisions based on the clustered data.
In summary, clusters are fundamental components of data mining that enable analysts to uncover hidden patterns and insights within large datasets. By leveraging clustering techniques effectively, organisations can make better-informed decisions, improve business processes, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.
Understanding Clusters in Data Mining: Definitions, Types, Analysis, and Examples
- What is cluster and types of cluster?
- What is cluster explain?
- What is cluster analysis and its types?
- What is cluster and its example?
What is cluster and types of cluster?
In the field of data mining, a cluster refers to a group of data points that exhibit similarities or share common characteristics within a dataset. Clustering is a technique used to identify these clusters and organise data points based on their intrinsic relationships. There are various types of clusters that can be formed during the clustering process, depending on the algorithm and criteria used. Common types of clusters include exclusive clusters (where each data point belongs to only one cluster), overlapping clusters (where data points can belong to multiple clusters), hierarchical clusters (which form a tree-like structure of nested clusters), and density-based clusters (which group data points based on their density in the dataset). Understanding the different types of clusters is essential for effectively applying clustering algorithms in data mining tasks and extracting valuable insights from complex datasets.
What is cluster explain?
In the context of data mining, a cluster refers to a group of data points that share similar characteristics or attributes. Clustering is a technique used to identify patterns and relationships within a dataset by grouping data points based on their similarities. Essentially, clusters help to organise and categorise data in a way that reveals underlying structures and trends. By understanding the concept of clustering and how it works, analysts can extract valuable insights from large datasets, leading to informed decision-making and improved understanding of complex data relationships.
What is cluster analysis and its types?
Cluster analysis is a fundamental technique in data mining that involves grouping data points into clusters based on similarities or patterns within the dataset. It aims to discover inherent structures in the data and identify relationships between data points. There are several types of cluster analysis methods, including partitioning methods like K-means clustering, hierarchical methods such as agglomerative clustering, density-based methods like DBSCAN, and model-based clustering algorithms. Each type of cluster analysis method has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of datasets and analytical goals. By understanding the various types of cluster analysis techniques, data miners can effectively extract meaningful insights from complex datasets and make informed decisions based on the clustered information.
What is cluster and its example?
In the context of data mining, a cluster refers to a group of data points that exhibit similarities or patterns based on certain characteristics or features. Clustering algorithms are used to identify these clusters, which can help analysts uncover hidden relationships and structures within a dataset. An example of clustering in data mining could be grouping customers based on their purchasing behaviour, where customers with similar buying patterns are clustered together. This clustering can provide valuable insights for targeted marketing strategies, customer segmentation, and personalised recommendations. By understanding what clusters represent and how they can be utilised, businesses can make more informed decisions and enhance their operations effectively.
No Responses