Scientific Study: The Importance of Research in Advancing Knowledge
Scientific study is a crucial aspect of advancing knowledge and understanding in various fields, from medicine to engineering to social sciences. It is through scientific research that new discoveries and breakthroughs are made, leading to the development of new technologies, treatments, and policies that can benefit society.
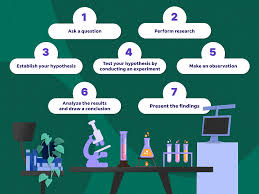
The scientific study involves a systematic approach to investigating phenomena or problems by collecting and analyzing data. This process includes developing hypotheses, designing experiments, collecting data, analyzing results, and drawing conclusions. The scientific method is designed to minimize bias and error in research, ensuring that results are reliable and accurate.
One of the most significant benefits of scientific study is its ability to provide evidence-based solutions to real-world problems. For example, medical research has led to the development of life-saving treatments for diseases such as cancer and HIV/AIDS. Engineering research has led to the creation of new technologies that have transformed industries such as transportation and energy production.
Moreover, scientific study plays a vital role in shaping public policy by providing policymakers with evidence-based recommendations. For example, environmental research has led to regulations aimed at reducing pollution levels in our air and waterways. Social science research has informed policies aimed at reducing poverty levels and improving access to education.
However, conducting scientific study is not without its challenges. Research can be expensive, time-consuming, and complex. Researchers must also navigate ethical considerations when working with human or animal subjects or handling sensitive information.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of scientific study far outweigh the costs. It is through rigorous research that we can expand our knowledge base and make progress towards solving some of society’s most pressing problems.
In conclusion, scientific study plays a critical role in advancing knowledge across various fields. From medicine to engineering to social sciences, researchers use a systematic approach to investigate phenomena or problems by collecting and analyzing data. Through their work, they develop evidence-based solutions that benefit society while navigating ethical considerations and challenges along the way.
Answers to Common Questions About Scientific Study
- What is the scientific method?
- How do I become a scientist?
- What are the benefits of scientific study?
- What are the different types of scientific research?
- How can I find reliable sources for scientific information?
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a process used by scientists to investigate phenomena or problems in a systematic and objective manner. It involves a series of steps that are designed to minimize bias and error in research and ensure that results are reliable and accurate.
The scientific method typically involves the following steps:
- Observation: Scientists observe a phenomenon or problem they want to investigate.
- Question: Scientists develop a question or hypothesis about the phenomenon or problem they observed.
- Hypothesis: Scientists develop a testable hypothesis, which is a tentative explanation for the observed phenomenon or problem.
- Experiment: Scientists design an experiment to test their hypothesis, which involves manipulating variables and measuring outcomes.
- Data analysis: Scientists collect data from their experiment and analyze it using statistical methods to determine if their hypothesis is supported by the evidence.
- Conclusion: Based on the data analysis, scientists draw conclusions about whether their hypothesis is supported or not supported by the evidence.
- Communication: Scientists communicate their findings through publications, presentations, or other means to share their results with other researchers and the public.
The scientific method is an iterative process, meaning that researchers often repeat these steps multiple times as they refine their hypotheses, experiments, and data analysis techniques. By following this rigorous process, scientists can ensure that their research produces reliable and accurate results that contribute to our understanding of the natural world.
How do I become a scientist?
Becoming a scientist requires a combination of education, skills, and experience. Here are some steps you can take to become a scientist:
- Pursue a Bachelor’s degree: Most scientists have at least a Bachelor’s degree in their field of study. Choose a major that aligns with your interests and career goals.
- Consider Graduate School: For many scientific fields, obtaining an advanced degree such as a Master’s or Ph.D. is necessary to advance in the field or conduct independent research.
- Gain Experience: Participate in internships, research programs, or other opportunities to gain hands-on experience in your field of study.
- Develop Skills: Scientists need excellent critical thinking skills, problem-solving skills, and analytical skills. They should also be proficient in data analysis and have strong communication skills.
- Network: Attend conferences or join professional organizations related to your field of study to meet other scientists and learn about new research developments.
- Publish Research: As you gain experience and knowledge in your field, consider publishing your research in academic journals to share your findings with the scientific community.
Remember that becoming a scientist is not an easy task and requires dedication and hard work. However, pursuing a career as a scientist can be incredibly rewarding as you contribute to expanding our knowledge of the world around us and making important discoveries that can benefit society as a whole.
What are the benefits of scientific study?
Scientific study has numerous benefits, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Scientific study aims to expand our understanding of the natural world, from the smallest particles to the largest galaxies. Through research, scientists can make new discoveries and uncover new information that can help us better understand ourselves and the world around us.
- Developing new technologies: Scientific study often leads to the development of new technologies that can transform industries and improve our quality of life. For example, medical research has led to life-saving treatments, while engineering research has resulted in innovative technologies such as electric cars and renewable energy sources.
- Improving health outcomes: Medical research is a key component of scientific study, with researchers working to develop treatments for diseases such as cancer, HIV/AIDS, and Alzheimer’s disease. This research helps improve health outcomes for individuals and populations.
- Informing public policy: Scientific study provides policymakers with evidence-based recommendations that can inform public policy decisions. For example, environmental research has led to regulations aimed at reducing pollution levels in our air and waterways.
- Enhancing education: Scientific study plays a vital role in enhancing education by providing students with opportunities for hands-on learning and critical thinking skills development.
- Fostering innovation: Scientific study encourages creativity and innovation by providing researchers with opportunities to explore new ideas and develop novel solutions to complex problems.
Overall, scientific study is essential for advancing knowledge across various fields while improving our quality of life through technological advancements and evidence-based policies.
What are the different types of scientific research?
There are various types of scientific research, each with its own goals, methods, and applications. Below are some of the most common types of scientific research:
- Basic research: This type of research aims to expand our understanding of fundamental principles and concepts in a particular field. Basic research is often curiosity-driven and does not have immediate practical applications.
- Applied research: This type of research aims to solve specific problems or develop new technologies that have practical applications. Applied research builds on the findings of basic research and seeks to translate them into real-world solutions.
- Quantitative research: This type of research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. Quantitative research is often used in fields such as psychology, economics, and medicine.
- Qualitative research: This type of research involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and case studies. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as anthropology, sociology, and education.
- Experimental research: This type of research involves manipulating one or more variables to determine their effect on a particular outcome. Experimental research is often used in fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology.
- Observational research: This type of research involves observing phenomena without manipulating any variables. Observational studies are often used in fields such as astronomy, ecology, and psychology.
- Longitudinal study: This type of study involves collecting data from the same group of individuals over an extended period to track changes over time. Longitudinal studies are often used in fields such as epidemiology and social sciences.
- Cross-sectional study: This type of study involves collecting data from a group at a single point in time to compare differences between groups or populations. Cross-sectional studies are often used in fields such as public health and social sciences.
Overall, each type of scientific research has its own strengths and limitations depending on the goals and questions being investigated. Researchers must carefully consider which type of research method is most appropriate for their specific research question and design their study accordingly.
How can I find reliable sources for scientific information?
Finding reliable sources for scientific information can be challenging, but it is essential to ensure that the information you are using is accurate and trustworthy. Here are some tips on how to find reliable sources for scientific information:
- Look for peer-reviewed articles: Peer-reviewed articles have been reviewed by experts in the field, and their findings have been deemed credible. You can find peer-reviewed articles in academic journals or through online databases such as PubMed or Google Scholar.
- Check the author’s credentials: It is important to ensure that the author of a scientific article has the necessary qualifications and expertise in their field. Look for authors who have published other works in reputable journals or who work at respected research institutions.
- Consider the funding source: Funding sources can influence research outcomes, so it is essential to consider who funded the study you are reading. Look for studies that were funded by reputable organizations such as government agencies or non-profit organizations.
- Evaluate the methodology: The methodology used in a study can affect its reliability and accuracy. Look for studies that use rigorous methods and controls, and avoid studies that make claims based on anecdotal evidence or small sample sizes.
- Consult multiple sources: It is always a good idea to consult multiple sources when researching a topic to ensure that you are getting a well-rounded understanding of the subject matter.
By following these tips, you can increase your chances of finding reliable sources for scientific information and avoiding misinformation or inaccurate claims.
No Responses